Having good knowledge about the boot sequence will be useful when troubleshooting a bricked android, flashing a custom ROM or rooting and etc. They are many device specific forum that did amazing write up on those topic, so i will not going to talk about it, but i will go through some of the basics on boot sequences in android, different boot mode in Android and how does rooting works on a unlocked bootloader phone. While researching on this topic, i stumbled upon a few interesting write up on rooting technique on a locked bootloader devices, maybe i will talk about that in near future .:)
Boot Sequence in android
- Boot loader - Stores the phone’s boot loader program that initialise the hardware and boot android kernel. It is usually manufacture’s proprietary code.
- Once boot loader has finished initialising the hardware it loads the Android kernel and initrd from the boot partition to RAM and it jumps into the Android kernel.
- Android kernel will run all the tasks needed for the Android system to run.
- Once all important tasks ran successfully, root file system will be mount and the first user-space process init.
- The init is the initial process for all other user-space processes. the init.rc will specifies the action to take while initializing the OS user space components. Such as starting services like Android Debug Bridge daemon(adbd., rild for telephony and so on.
- Zygote will start Dalvik VM and start the first Java component System server.
- Other Android Framework Services Manager such as Telephony Manager will be started.
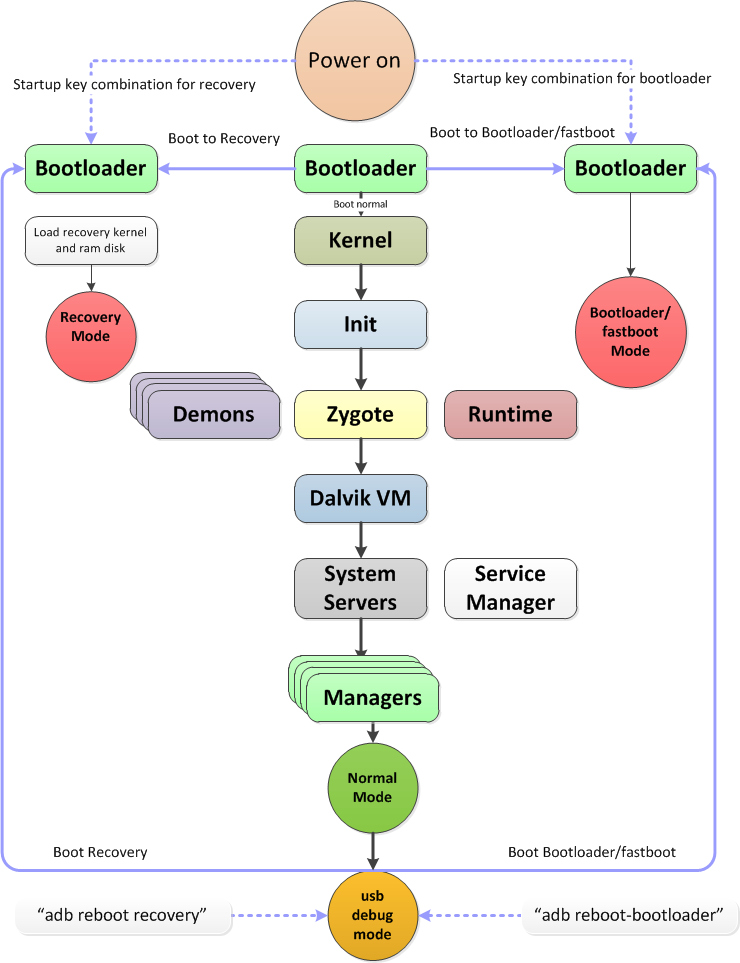
Download mode
Download mode allow user to update the persistent storage at a low level through a process typically called flashing. It normally be available via fasboot protocol.
Recover mode
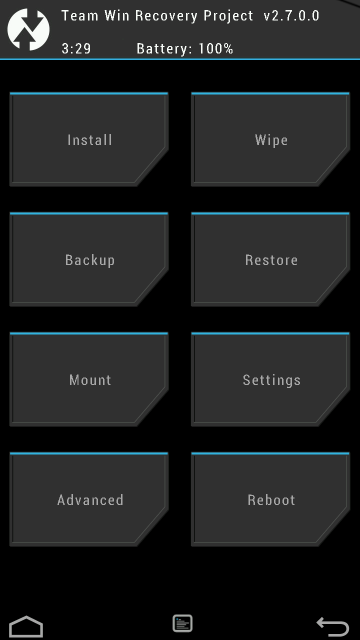
Stores a minimal Android boot image that provides maintenance functions and serves as a failsafe. Many power user prefer to flash a custom recovery on their device such as Clorkworkmod, TWRP and etc. A custom recovery will provide the same functionality the default recovery mode but it has some additional function such as back up and recover device, install custom ROM and many more. figure below shows a sample screenshot from TWRP.
PS: If you have the need to provision multiple device with the same setup, you can back up your device with tools like twrp and recover it on other devices.
Locked and unlocked boot loaders
Locked boot loaders prevents end user from performing modifications the device firmware by implementing restrictions at the boot loader level. It usually has a cryptographic signature verification that prevents booting or flashing unsigned code to the device. Unlocking a boot loader carries serious security implications, if the device is lost or stolen, all data on it can be recovered by an attacker by uploading a custom android boot image or flashing a custom recovery image and will be granted with full access on the device’s partitions.
How to lock your unlocked Android devices
#boot into fastboot
adb reboot recovery
#check boot loader lock status
fastboot oem device-info
#lock boot loader
fastboot oem lock
Recovery Images
The Android recovery system is Android’s standard mechanism that allows software updates to replace the entirety of the system software preinstalled on the device without wiping user data.
Rooting with an Unlocked Boot loader
You can modify a factory image to add an su binary. In this example, we unpack an ext4 formatted system image, mount it, add an su binary, and repack it. If we ash this image, it will contain the su binary and the device will be rooted.
mkdir systemdir
simg2img system.img system.raw
mount -t ext4 -o loop system.raw systemdir
cp su systemdir/xbin/su
chown 0:0 systemdir/xbin/su
chmod 6755 systemdir/xbin/su
make_ext4fs -s -l 512M -a system custom-system.img systemdir
umount systemdir
Comments
comments powered by Disqus